|
|
 |
Transfer of Energy |
|
|

 |
 |
 |
In some materials, such as metals, electrons flow easily, where as in insulated materials such as glass they can hardly flow at all. Semiconducting materials have intermediate behavior. At low temperatures, some materials become superconductors and offer no resistance to the flow of electrons. |
|
|
 |
The electric force is a universal force that exists between any two charged objects.
Opposite charges attract while like charges repel. The strength of the force is proportional to the charges, and as with gravitation, inverse with proportion to the square of the distance between them. |
|
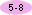 |
Electrical circuits provide a means of transferring electrical energy when heat, light, sound, and chemical changes are produced. |
|
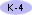 |
Electricity in circuits can produce light, heat, sounds, and magnetic effects. Electrical circuits require a complete loop through which an electrical current can pass. |
|
|
|
|